Nikoo Samadi
What is EDI in ERP? The answer for distributors and manufacturers is the key to the difference between moving smoothly or getting stuck with costly delays. Orders, shipments, and invoices pass through a supply chain where mistakes aren’t allowed. Old processes slow things down, cause errors, and block growth.
When EDI runs inside an ERP system like Business Central, data moves automatically. The result is fewer mistakes, faster processing, and more time for teams to spend on important work. In industries like retail and manufacturing where every hour and every margin matter, this kind of efficiency makes a clear difference.
What is EDI in ERP Systems?
EDI stands for Electronic Data Interchange. It is the computerized transfer of business documents (like purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices) between organizations in pre-agreed formats. It does this without paper, without re-typing.
In ERP systems, the data exchange process allows for the automatic flow of information from partner systems straight into the ERP. The ERP then uses the information to replenish inventory, process invoices, or initiate shipments. Zero manual entry equals reduced errors, quicker operations.
Standard formats (such as EDIFACT, ANSI X12) make a point of having the document structured in a form familiar to both systems. These define what goes in the document and where, what fields you must include, how you must format quantities and dates, and so on.
Because document interchange is facilitated automatically by this structured document exchange in ERP applications, businesses enjoy more reliable data, shorter processing periods, and more fluid processes. Business entities employing EDI in their ERP are better equipped to process high transaction volumes without any delays.
Simplify Your Decision with GEM365
Get in touch with GEM365 to guide you through the process and get consultation for free.
For example, Wayne Pipe and Supply had already put EDI into place, but their numerous vendors found it difficult to use due to its rigidity. Some lacked or had non-standard data mapping; in certain cases, the documents were not even readable by humans, and IT was plagued by constant errors. To address these issues, the company migrated to IDEA Exchange, a managed EDI service. Important changes include:
- Adding additional EDI transaction types (such as purchase order modifications and order acknowledgments) to enable the automatic flow of more supporting documentation.
- A better interface between their ERP and EDI system that allows the ERP to be updated automatically without human input as soon as a document is received.
- Increased visibility: Without knowing how to code, non-IT employees could more easily identify errors and view the EDI messages in a human-readable format.
Results:
- There was a notable decrease in order processing errors.
- A shorter turnaround time for vendor orders (some used to take days, but now only take one day).
- Less time was spent on internal paper sorting and error correction.
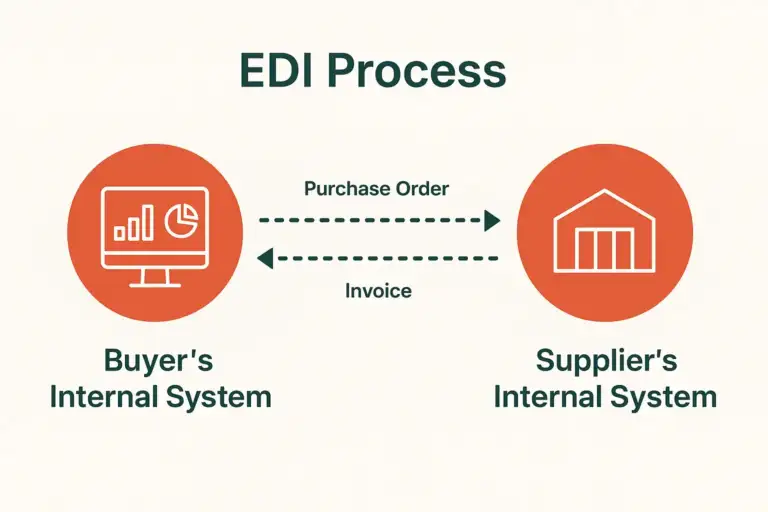

The Role of EDI Integration in ERP
EDI integration in ERP means the ERP and EDI system work together as one. Instead of processing documents in two separate tools, the ERP receives and sends data directly. A purchase order from a customer creates a sales order in the ERP.
This kind of integration reduces manual effort and redundant records. It also provides consistency of information across departments: sales, accounting, logistics, and customer service all see the same information at the same time.
Data Interchange states that businesses that integrate EDI directly with ERP reduce costs and eliminate delays because data flows without human intervention. Errors that once required back-and-forth phone calls or emails no longer occur.
Without it, staff spend time chasing paper instead of focusing on production and service. That’s why many manufacturers and distributors, when asking what is EDI in ERP, point to integration as the most critical factor.
Looking to connect EDI with Microsoft Dynamics ERP? Learn more at gem365.ca
ERP and EDI Efficiency in Production and Distribution
The speed and accuracy of information flow determine manufacturing and distribution efficiency. Every delay—a late order, an incorrectly scheduled shipment—increases expenses and erodes consumer confidence.
Efficiency is one of the most obvious responses that companies give when they ask what EDI in ERP is. With integration established:
- Order processing becomes faster: A purchase order is sent through an automated data exchange. from a retailer. The ERP immediately prepares shipping, updates inventory, and generates a sales order. It now only takes minutes to complete tasks that used to require hours of manual labor.
- Mistakes happen: Since no one retypes the data, typos in item numbers or quantities vanish. When the ERP receives structured data, it always uses it in the same manner.
- Visibility gets better. Teams in purchasing, production, and logistics see the same figures when orders, invoices, and shipping notifications are processed in real time through ERP. Current data, not estimates, is used to make decisions.
According to a Data Interchange report, this approach within ERP lowers expenses associated with data entry and reconciliation for businesses. Not only do the savings result from fewer errors, but they also free up employees to concentrate on more important work.
This may result in improved production scheduling for manufacturers. It means more dependable shipping windows for distributors. In both situations, efficiency now involves moving precise information at the appropriate moment rather than just moving goods.
EDI-Powered ERP Automation: Revolutionizing Operations
Automation is one of the most useful responses that businesses give when they are asked what EDI in ERP is. ERP systems can exchange documents without human input thanks to EDI. When a purchase order, shipping notice, or supplier invoice is transferred from one business to another, it automatically updates the ERP and initiates the subsequent action.
Automating the exchange of documents, such as purchase orders and invoices, reduces delays. Without waiting for employees to take action, the ERP can post transactions, modify stock levels, or schedule production as soon as it receives structured EDI data.
In terms of manufacturing, this means that the proper materials are used on production lines. It means that shipments with proper documentation depart on schedule for distribution. Processes that previously required hours of administrative labor are transformed into real-time updates through ERP automation with EDI.
Speed and dependability are the outcomes. In addition to increasing efficiency, businesses also obtain consistent records that facilitate improved supply chain planning and compliance.
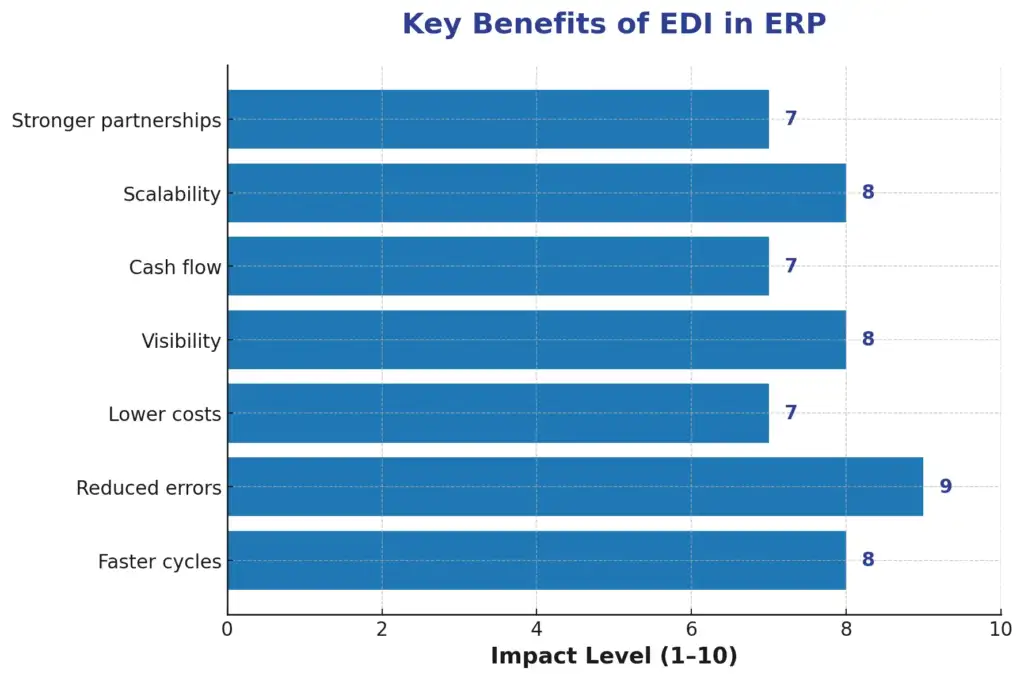
The Key Benefits of EDI in ERP
The benefits of EDI in ERP make it obvious why so many companies choose to use it. The main benefits supported by current sources are as follows:
- Quicker cycles of business
Delays are reduced by automating the exchange of documents, such as purchase orders and invoices. TrueCommerce claims that EDI-ERP integration eliminates the need for multi-step review and manual data entry. - Lower rates of errors
EDI regulates structure and validation. Document fields follow to certain guidelines. Therefore, there will be fewer typos, mistakes, and disagreements. Following integration, Celigo reports a 90% decrease in manual order entry. - Greater understanding of the supply chain
Internal and partner-facing data reside in the same system when EDI is integrated with ERP. This provides companies with up-to-date information on everything from vendor performance to inventory levels. According to Remedi, you can more effectively manage resources and identify possible disruptions earlier. - Improved cash flow and financial efficiency
Faster invoice and payment processing makes money move more smoothly, with fewer delays. Celigo notes that the integration of EDI and ERP improves the cycles of accounts payable and receivable. - Scalability
An EDI-enabled ERP handles growth better as transaction volume increases (more purchase orders, more vendors, more partners). As scale grows, less manual labor is required. - Improved relationships with partners
Standard formats, dependable document exchange, and fewer errors help build trust with suppliers, customers, and trading partners. Better partner onboarding and fewer disputes are highlighted by both Orderful and TrueCommerce.

How EDI Helps Business Central Improve ERP
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central shows how EDI and ERP function together in real-world scenarios for businesses unsure about what EDI in ERP is:
- Data centralization
Business Central keeps data and documents in one location rather than across different systems by integrating EDI integrations with ERP workflows. - ERP integration of EDI
Purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notifications are examples of incoming EDI documents that directly create or update records in the ERP. This speeds up supply chain procedures and reduces manual hand-offs. - ERP and EDI effectiveness
Everyone uses the same exact information thanks to real-time updates, including accounting, purchasing, and warehouse employees. Any changes to a distributor’s order are instantly reflected throughout the ERP. - ERP automation with EDI
Routine processes like order acknowledgments, shipping notifications, and invoicing are automated by ERP automation with EDI Business Central. Without staff involvement, transactions proceed through the ERP. - Benefits of EDI in ERP
Business Central, which is cloud-based and scalable, facilitates the main advantages of EDI in ERP, including reduced IT overhead, faster processing, fewer errors, and compliance with trading partners.
Final Thoughts
The answer to the question of what EDI in ERP is straightforward: it’s a method of accurately and swiftly moving business documents without the need for human labor. This translates into smoother supply chains, fewer errors, and fewer delays for producers and distributors. When incorporated into a system such as Business Central, EDI improves processes and gives businesses the dependability and efficiency they need to remain competitive.
Table of Contents
Read more


Forbes Reveals the Best Cloud ERP: Here’s Why Business Central Wins


How the Microsoft Power Apps Platform Transforms Manual Processes


Top Power Automate Workflows Every Business Should Use in 2025









