What Is Microsoft Power Apps?
Microsoft Power Apps is a low-code application development platform designed for building custom business applications with minimal traditional coding. It enables organizations to create applications that connect to data, support business processes, and run across web and mobile devices.
At its core, it provides tools for designing application interfaces, connecting to data sources, and defining logic that controls how an app behaves. These applications can use data stored in Microsoft Dataverse or connect to external systems such as SharePoint, SQL Server, Microsoft Excel, and many other cloud and on-premises services through built-in connectors.
Applications created with Power Apps are typically used to support internal operations, manage data entry, streamline workflows, or replace manual and spreadsheet-based processes. Once published, apps can be accessed securely by users through browsers or mobile devices, using Microsoft Entra ID for authentication and access control.
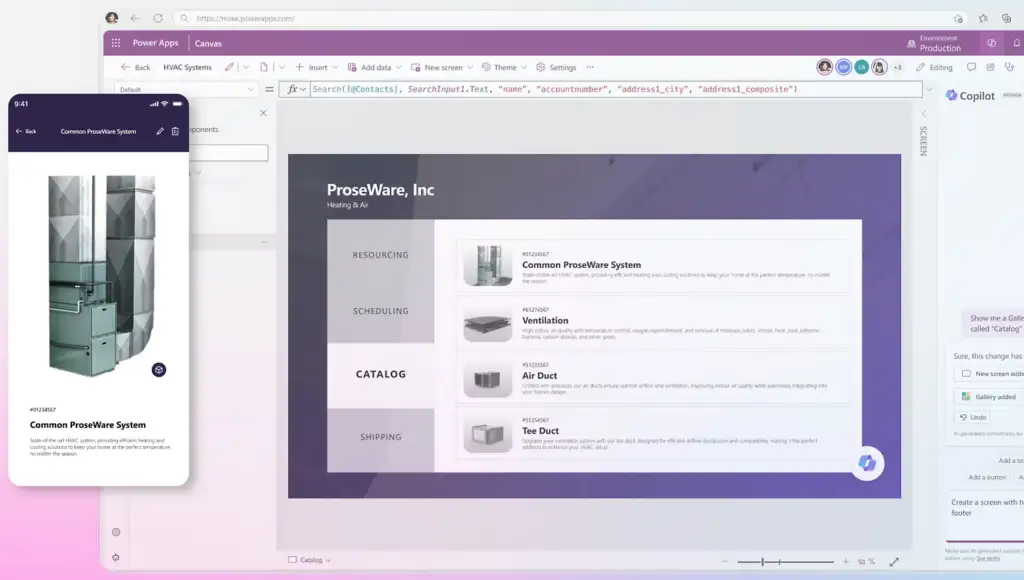


Power Apps as a Low-Code Application Platform
Power Apps is positioned as a low-code application platform, meaning it allows applications to be built using visual design tools and declarative logic rather than extensive custom code. App creators define user interfaces, data connections, and behavior through configuration, expressions, and reusable components, reducing the need for traditional software development methods.
The platform provides a design environment where applications are created using drag-and-drop controls, prebuilt templates, and formulas that resemble spreadsheet logic. This approach makes it possible to model application behavior, validate input, and manage data interactions without writing full application code.
While Power Apps emphasizes low-code development, it also supports extensibility through custom connectors, APIs, and integration with Azure services. This allows applications to range from simple data-entry tools to more advanced solutions that interact with enterprise systems, while still being developed and maintained within a low-code framework.
Core Functions of Microsoft Power Apps
Power Apps provides a set of core functions that support the creation, management, and operation of business applications. These functions define how applications are designed, how they connect to data, and how logic and access are handled within the platform.
Application Design and User Interface
This platform includes visual design tools for building application interfaces. App creators can define screens, forms, and navigation using configurable controls, allowing applications to be structured without writing traditional UI code.
Data Connectivity
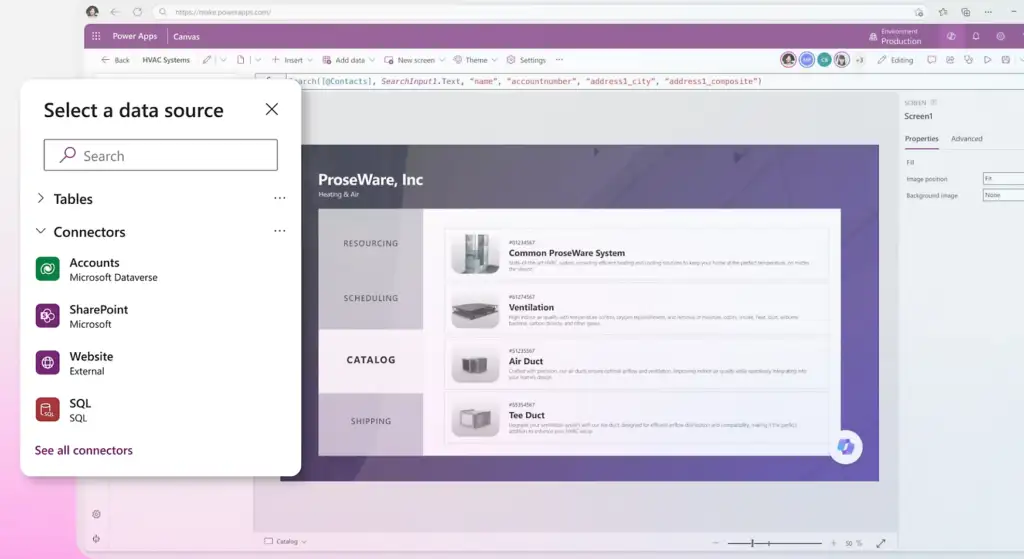
The low-code platform enables applications to connect to data stored in Microsoft Dataverse and external systems. Built-in connectors allow apps to read and write data from services such as SharePoint, SQL Server, Microsoft Excel, and other supported sources.
Business Logic and Formulas
Power Apps supports the definition of application behavior through formulas and expressions. These formulas control validation rules, calculations, conditional visibility, and interactions between data and user actions.
Integration with Microsoft Services
Applications built with Power Apps can integrate with other Microsoft services across the Power Platform and Microsoft 365. This allows apps to work alongside tools such as Power Automate, Power BI, and Dynamics 365.
Application Publishing and Access
Once an application is created, it can be published and shared with users through web browsers or mobile devices. Access is managed through Microsoft Entra ID, ensuring applications follow organizational identity and security policies.
Turn Business Requirements into Power Apps Solutions
Contact our team to discuss application design, data integration, and deployment strategies using Microsoft Power Apps.
What Problems Does Power Apps Solve
Organizations commonly face challenges when managing business processes using manual or disconnected tools. Power Apps is designed to address scenarios such as:
Dependence on spreadsheets and manual tools
Many teams rely on Excel files or ad-hoc tools to manage processes. Over time, these solutions become difficult to maintain, version, and control as usage increases.Email-based approvals and workflows
Processes that run through emails often lack visibility, tracking, and consistency. This platform enables organizations to move these workflows into structured applications.Inconsistent data entry and validation
When data is collected through informal methods, it is hard to enforce rules and standards. Power Apps allows data to be captured, validated, and stored in a controlled and consistent way.Delays in adapting to changing requirements
Small updates to forms or processes often require technical changes or system customization. Microsoft’s low-code platform allows applications to be adjusted without rebuilding entire systems.Gaps in existing systems
Core platforms may not fully support specific operational needs. Power Apps can be used to build targeted applications that integrate with existing data sources and workflows.



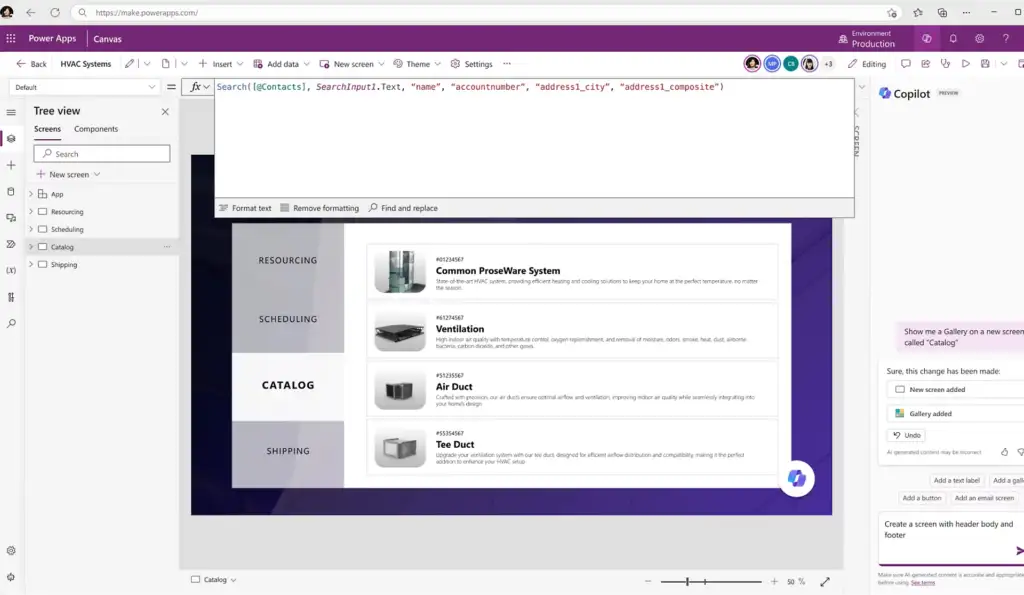
How Power Apps Works
Power Apps follows a structured approach for building and running business applications. While the platform supports advanced scenarios, the core process can be understood in a few key stages.
Connect to data sources
This platform starts by connecting to data. Applications can use data stored in Microsoft Dataverse or connect to external systems such as SharePoint, SQL Server, Microsoft Excel, and other supported services through built-in connectors.Design the application interface
App creators define how users interact with the application by designing screens, forms, and navigation. Visual components are used to control how data is displayed and entered, without requiring traditional interface coding.Define logic and behavior
Application behavior is controlled through formulas and rules. These determine how data is validated, how calculations are performed, and how the app responds to user actions such as selections or submissions.Integrate with other Microsoft services
Power Apps can work alongside other tools within the Microsoft ecosystem. This allows applications to interact with workflows, reporting, and business processes managed through related Microsoft services.Publish and access the app
Once an application is ready, it is published and made available to users. Apps can be accessed through a web browser or mobile devices, with authentication and access managed through Microsoft Entra ID.
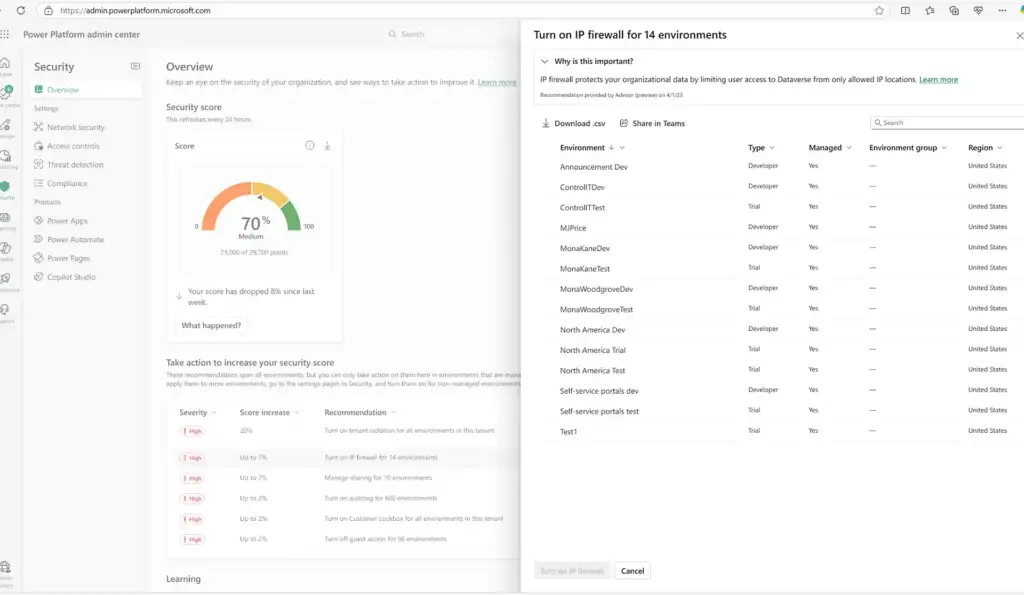
Security and Governance in Power Apps
Security and governance are key considerations for any organization building applications with Power Apps. The platform provides multiple layers of control to ensure that data and applications are managed safely and comply with organizational policies.
Environment Strategy
Power Apps uses environments to separate development, testing, and production apps. Organizations can control access to each environment and manage which apps and data resources are available to different teams.Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Access to apps and data is managed using Microsoft Entra ID roles. Administrators can assign users or groups specific permissions to ensure that sensitive data is protected and only authorized users can perform certain actions.Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Policies
DLP policies allow organizations to control which connectors and data sources can be used together. This ensures that business-critical or sensitive information is not exposed through apps or workflows.Auditing and Monitoring
Power Apps provides tools for tracking app usage, changes, and user activity. These logs help organizations monitor compliance, identify unusual activity, and maintain accountability.Governance Best Practices
Organizations can implement strategies such as naming conventions, environment segregation, and lifecycle management to maintain consistency, reduce errors, and simplify maintenance across multiple apps.



Licensing Overview
Power Apps licensing can seem complex, but understanding the main options helps organizations choose the right plan for their needs. Licensing is based on either per-user or per-app models and is often included with certain Microsoft 365 or Dynamics 365 subscriptions.
Per App Plan
Allows a user to run one or two specific apps within a single environment. Ideal for organizations with targeted business solutions that do not require full platform access.Per User Plan
Grants a user the ability to run unlimited apps across multiple environments. Suitable for employees who need broad access to multiple business applications or require flexibility to use apps in various workflows.Included Licenses
Some Microsoft 365 and Dynamics 365 subscriptions include Power Apps access with limited functionality. Users can create and run apps within these limits without purchasing an additional license.Add-Ons and Extensions
Advanced features such as premium connectors, integration with Dataverse, or AI Builder capabilities may require add-ons to the base license. Organizations can scale licensing to match app complexity and usage requirements.Governance Considerations
Licensing choices should align with environment strategy and governance policies. Tracking who has access to premium features and ensuring compliance with organizational rules is key to cost-effective deployment.
Implementation and Deployment
Implementing Power Apps involves planning, development, testing, and deployment. Proper governance and environment strategy help organizations deliver applications efficiently while maintaining security and compliance.
Environment Planning
Define separate environments for development, testing, and production. This ensures apps can be developed and validated safely before being shared with end users.App Development Lifecycle
Power Apps supports iterative development using low-code tools. Teams can design screens, define logic, and connect to data sources while testing functionality throughout the development process.Testing and Validation
Applications should be tested for usability, data integrity, and integration with other systems. Testing helps ensure that apps perform as expected and align with organizational workflows.Deployment and Sharing
Once validated, apps can be published to production environments. Users access apps through browsers or mobile devices, with permissions controlled via Microsoft Entra ID.Monitoring and Maintenance
After deployment, administrators can monitor app usage, update logic, and make changes as business requirements evolve. Regular maintenance ensures apps remain reliable and compliant.Integration with ALM Practices
Power Apps supports Application Lifecycle Management (ALM), enabling version control, solution packaging, and environment promotion to streamline ongoing updates and governance.


FAQ Microsoft Power Apps
This platform can connect to a variety of data sources, including Microsoft Dataverse, SharePoint lists, SQL Server, Excel files, and many online services via built‑in connectors. This allows apps to work with live business data in real time.
Yes. Applications built with Power Apps can be accessed by users through modern web browsers and on mobile devices (iOS and Android) using the Power Apps mobile app.
Yes. This platform integrates seamlessly with Power Automate to automate workflows, approvals, notifications, and other processes triggered by user actions in the app.
Microsoft provides built‑in support options through the Power Apps portal, including technical support plans and documentation. You can also access community forums, tutorials, and official Microsoft Learn resources for guidance.

